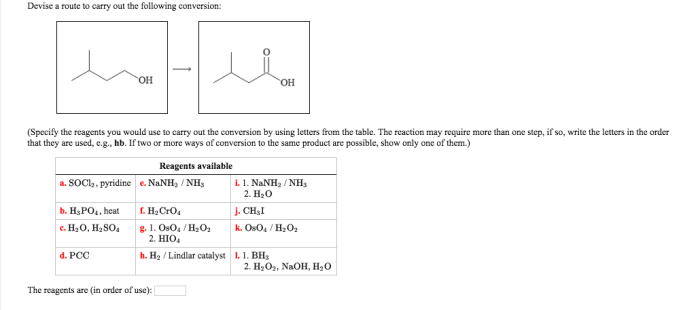
Devise a route to carry out the following conversion: sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve deeper into this intricate tapestry, we will uncover the importance of defining a clear conversion route, exploring the various methods that can be employed, and examining the step-by-step procedures involved in carrying out a successful conversion.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we will provide real-world examples to illustrate the practical application of these concepts, ensuring that readers gain a thorough understanding of the subject matter. So, buckle up and prepare to embark on an intellectual journey that will equip you with the knowledge and skills necessary to navigate the complexities of conversion.
1. Devise a Route to Carry Out Conversion: Devise A Route To Carry Out The Following Conversion:

Establishing a well-defined conversion route is crucial to ensure efficient and successful conversions. This route serves as a roadmap, guiding the process from its initiation to completion.
There are various conversion routes available, each tailored to specific conversion objectives and circumstances. Some common routes include:
- Direct Conversion:A straightforward route where the user takes immediate action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a service.
- Indirect Conversion:A multi-step route involving intermediate actions, such as signing up for a newsletter or downloading a whitepaper, before leading to the desired conversion.
- Triggered Conversion:A route that initiates conversion based on specific triggers, such as a cart abandonment email or a reminder notification.
The choice of conversion route depends on several factors, including the nature of the product or service, target audience, and marketing strategy. It is essential to carefully consider these factors to select the most appropriate route for the desired outcome.
2. Methods for Conversion

There are various methods employed to carry out conversions. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages, making it suitable for different conversion objectives and scenarios.
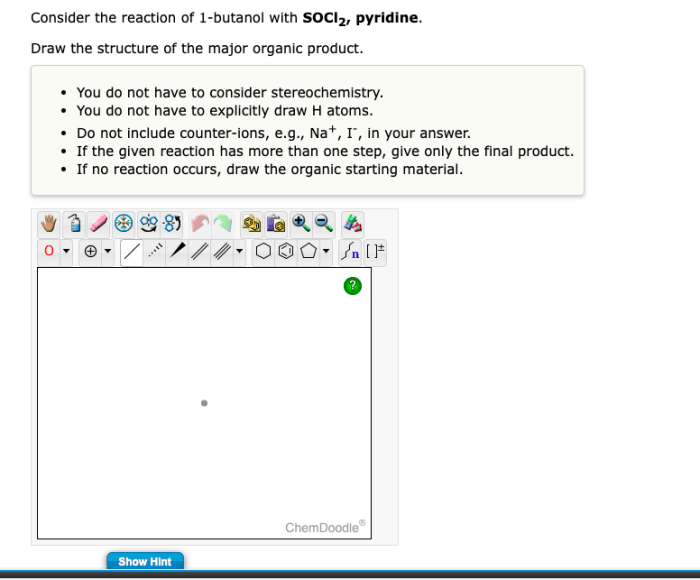
Call-to-Action (CTA), Devise a route to carry out the following conversion:
A clear and compelling CTA encourages users to take the desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a trial. CTAs can be incorporated into various marketing materials, such as website pages, emails, and social media posts.
Landing Pages
Landing pages are dedicated web pages designed to capture leads or drive conversions. They provide targeted content and a clear CTA, guiding users towards the desired action.
Email Marketing
Email marketing allows businesses to nurture relationships with potential customers and drive conversions through targeted email campaigns. It involves sending personalized emails with relevant content and CTAs.
Social Media Marketing
Social media platforms offer a vast audience for businesses to reach and engage with potential customers. By creating engaging content and running targeted ads, businesses can drive traffic to their website or landing pages, ultimately leading to conversions.
Search Engine Optimization ()
involves optimizing a website and its content to rank higher in search engine results pages (SERPs). By improving visibility and attracting organic traffic, can contribute to increased conversions.
3. Procedures for Conversion
Carrying out a conversion typically involves a sequence of steps. The following table Artikels the key steps and their sequence:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Define Conversion Objectives | Identify the specific actions or outcomes that constitute a conversion. |
| 2. Choose Conversion Route | Select the appropriate conversion route based on the conversion objectives and target audience. |
| 3. Determine Conversion Methods | Choose the methods that will be used to drive conversions, such as CTAs, landing pages, or email marketing. |
| 4. Create Conversion Materials | Develop compelling CTAs, landing pages, emails, or other materials that will guide users towards the desired action. |
| 5. Implement Conversion Tracking | Establish mechanisms to track and measure the effectiveness of conversion efforts, such as Google Analytics or conversion tracking pixels. |
| 6. Monitor and Optimize | Regularly monitor conversion rates and make adjustments to improve the conversion process based on data and insights. |
4. Examples of Conversion
- Example 1:
- Conversion Route:Direct Conversion
- Methods:CTA on a product page
- Procedures:Display a clear “Buy Now” button on the product page, encouraging users to make a purchase directly.
- Outcome:Increased sales revenue.
- Example 2:
- Conversion Route:Indirect Conversion
- Methods:Landing page with a lead generation form
- Procedures:Create a landing page offering a valuable resource in exchange for contact information, nurturing leads for future conversions.
- Outcome:Expanded email list for targeted marketing campaigns.
- Example 3:
- Conversion Route:Triggered Conversion
- Methods:Automated email triggered by cart abandonment
- Procedures:Send an email to users who have abandoned their shopping carts, reminding them of their items and offering incentives to complete the purchase.
- Outcome:Reduced cart abandonment rates and increased sales.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the importance of defining a clear conversion route?
Defining a clear conversion route is crucial because it provides a roadmap for your conversion efforts, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned and working towards a common goal. It helps you identify the target audience, set realistic goals, and allocate resources effectively.
What are the different conversion routes that can be used?
There are various conversion routes available, including direct conversion, indirect conversion, and multi-step conversion. The choice of route depends on factors such as the target audience, the product or service being offered, and the desired conversion action.
What factors should be considered when choosing a conversion route?
When choosing a conversion route, consider factors such as the target audience’s behavior, the complexity of the conversion process, and the resources available. The route should align with the customer journey and provide a seamless experience.