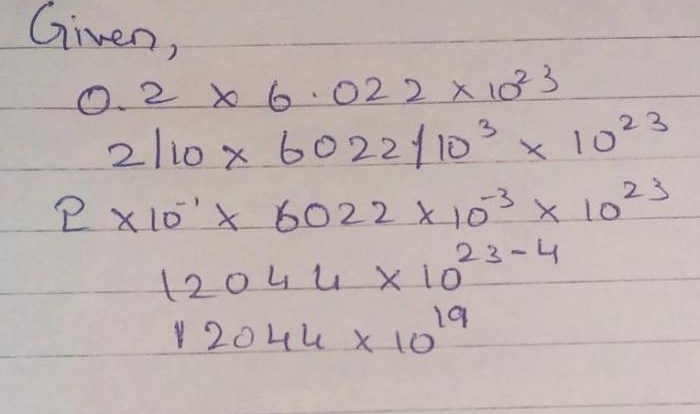Introducing our ‘Mole to Mole Ratio Worksheet’, a valuable resource designed to simplify and reinforce your understanding of this crucial chemistry concept. This worksheet will guide you through the basics, applications, and advanced uses of mole to mole ratios, equipping you with the knowledge to excel in your studies.
Dive into the fascinating world of stoichiometry and chemical reactions, where mole to mole ratios play a central role in balancing equations, determining limiting reactants, and predicting reaction yields. Get ready to enhance your problem-solving skills and deepen your comprehension of chemical principles.
Mole to Mole Ratio Basics
In chemistry, the mole is the standard unit for measuring the amount of a substance. It is defined as the amount of a substance that contains exactly 6.022 × 10 23elementary entities of that substance. These entities can be atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons.
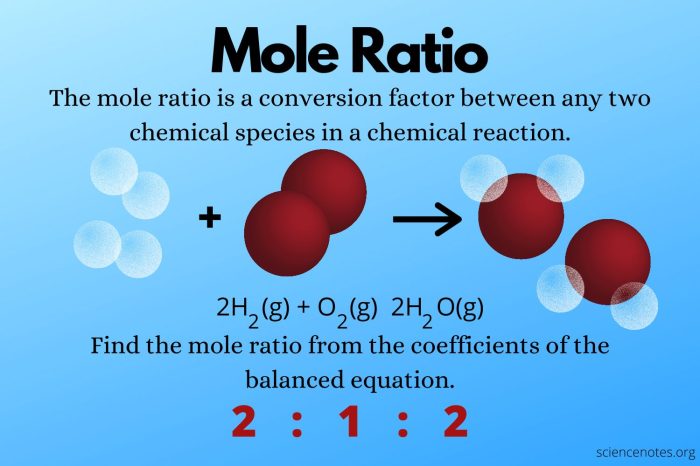
A mole-to-mole ratio is a ratio that compares the number of moles of two different substances involved in a chemical reaction. It is used to determine the stoichiometric coefficients in a balanced chemical equation.
Just when you thought you’d mastered mole to mole ratios, let’s switch gears and test your knowledge of the foramina of the skull. Head over to this foramina of the skull quiz and put your anatomical knowledge to the test.
Once you’ve aced that, come back and let’s continue our exploration of mole to mole ratios.
Examples of Mole to Mole Ratios
For example, in the following balanced chemical equation:
2 H 2+ O 2→ 2 H 2O
The mole-to-mole ratio of hydrogen (H 2) to oxygen (O 2) is 2:1. This means that for every 2 moles of hydrogen that react, 1 mole of oxygen is required.
Using Mole to Mole Ratios
Mole to mole ratios are a fundamental tool in stoichiometry, enabling us to determine the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. By understanding and applying these ratios, we can balance chemical equations and make accurate predictions about the amounts of substances involved in a reaction.
Using Mole to Mole Ratios to Balance Chemical Equations
Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting the coefficients in front of each chemical formula to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation. Mole to mole ratios provide the basis for this process.
For example, consider the unbalanced equation:
C2H 6+ O 2→ CO 2+ H 2O
To balance this equation, we can use the mole to mole ratio between C 2H 6and O 2, which is 1: 3. This means that for every 1 mole of C 2H 6that reacts, 3 moles of O 2are required.
Similarly, the mole to mole ratio between C 2H 6and CO 2is 1:2, indicating that 1 mole of C 2H 6produces 2 moles of CO 2. Using these ratios, we can balance the equation as follows:
C2H 6+ 3O 2→ 2CO 2+ 3H 2O
Practice Problems
- Balance the following equation using mole to mole ratios:
Fe + HCl → FeCl2+ H 2
- Determine the mole to mole ratio between NaOH and HCl in the following reaction:
NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2O
Mole to Mole Ratio Worksheet Activities
Mole to mole ratio worksheet activities are designed to help students practice using mole to mole ratios to solve stoichiometry problems. These worksheets can be used as a formative assessment tool to check for understanding or as a review tool to help students prepare for exams.
Worksheet Design
When designing a mole to mole ratio worksheet, it is important to include a mix of difficulty levels. This will help to ensure that all students are challenged and that they are able to practice the skills they need to master.
Some problems can be more straightforward, while others can be more complex and require students to apply multiple concepts.
It is also important to provide answer keys or solutions to the problems. This will help students to check their work and to identify any areas where they need additional practice.
Worksheet Activities
Here are some mole to mole ratio worksheet activities that you can use in your classroom:
- Basic mole to mole ratio problems:These problems ask students to convert between moles of reactants and moles of products using the mole to mole ratios in the balanced chemical equation.
- Limiting reactant problems:These problems ask students to identify the limiting reactant in a reaction and to calculate the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
- Percent yield problems:These problems ask students to calculate the percent yield of a reaction, which is the actual yield divided by the theoretical yield.
Advanced Applications of Mole to Mole Ratios
Mole to mole ratios find extensive applications in various chemical calculations, including determining limiting reactants, excess reactants, and reaction yields. These ratios are crucial for predicting the outcome of chemical reactions and optimizing reaction conditions.
Limiting Reactants and Excess Reactants
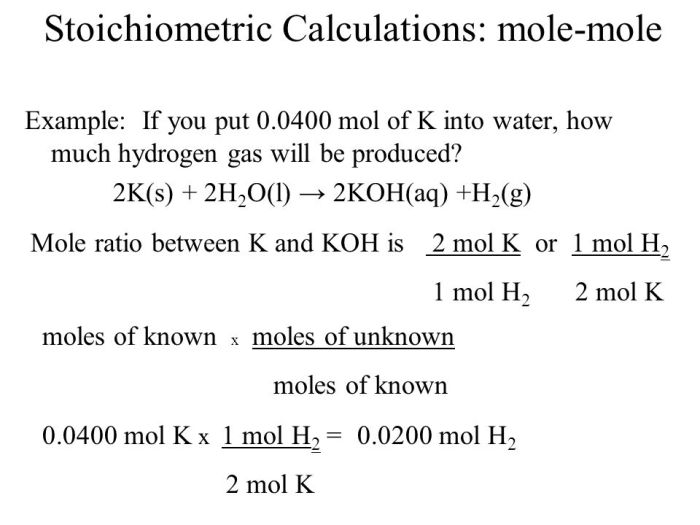
In a chemical reaction, the limiting reactant is the one that is entirely consumed, thereby limiting the amount of product formed. The excess reactant is the one that remains after the reaction is complete. To determine the limiting reactant, we compare the mole ratio of the reactants to their stoichiometric ratio.
The reactant with the smallest mole ratio relative to its stoichiometric coefficient is the limiting reactant.
Reaction Yields, Mole to mole ratio worksheet
The reaction yield is the amount of product obtained relative to the theoretical maximum amount that could be formed. Mole to mole ratios help determine the yield by comparing the actual moles of product formed to the moles of limiting reactant used.
The yield is often expressed as a percentage and provides insights into the efficiency of the reaction.
Real-World Applications
Mole to mole ratios have numerous real-world applications, including:
-
-*Chemical synthesis
Determining the correct proportions of reactants to achieve desired product yields.
-*Environmental monitoring
Calculating the amount of pollutant released into the environment based on the mole ratio of reactants in a chemical process.
-*Medicine
Determining the appropriate dosage of drugs based on the mole ratio of active ingredients to inactive ingredients.
Visual Aids for Understanding Mole to Mole Ratios: Mole To Mole Ratio Worksheet
Visual aids can be powerful tools for comprehending mole to mole ratios. They provide a concise and easily digestible representation of the concepts, making them accessible to learners of all levels.
Table: Key Concepts of Mole to Mole Ratios
This table summarizes the fundamental principles of mole to mole ratios:
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Mole to Mole Ratio | A ratio that relates the number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. |
| Balanced Chemical Equation | An equation that shows the mole ratios of reactants and products. |
| Stoichiometry | The study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in a chemical reaction. |
| Limiting Reactant | The reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed. |
| Excess Reactant | The reactant that is present in excess after a chemical reaction, meaning some of it remains unreacted. |
Flowchart: Using Mole to Mole Ratios
The following flowchart Artikels the steps involved in using mole to mole ratios:
- Write a balanced chemical equation.
- Convert the given mass or volume of a reactant to moles.
- Use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to determine the moles of other reactants or products.
- Convert the moles of the desired substance to mass or volume (if necessary).
Images and Diagrams
Visual representations can further enhance the understanding of mole to mole ratios:
- Molecules and Moles:Diagrams can illustrate the concept of a mole as a specific number of molecules (e.g., Avogadro’s number).
- Balanced Chemical Equations:Structural formulas can visually represent the mole ratios of reactants and products in a balanced chemical equation.
- Stoichiometry Problems:Diagrams can depict the conversion of reactants to products, highlighting the mole ratios involved.
FAQ Resource
What is a mole to mole ratio?
A mole to mole ratio is a relationship between the moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. It helps us determine the stoichiometric proportions of reactants needed to react completely.
How do I use mole to mole ratios to balance chemical equations?
By comparing the moles of reactants and products, we can adjust the coefficients in a chemical equation to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides.
What are limiting reactants?
Limiting reactants are the reactants that are completely consumed in a chemical reaction, limiting the amount of product that can be formed.